Arthritis
Arthritis is a term that refers to inflammation of one or more joints, resulting in pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased joint mobility..
There are many types of arthritis, but the two most common ones are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis..
-
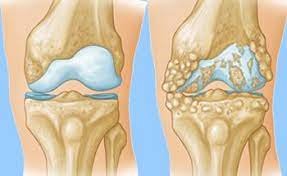
Osteoarthritis (OA):
-
Causes: Osteoarthritis is often associated with the wear and tear of joints over time. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down, leading to pain, swelling, and problems with joint movement.
-
Risk Factors:
- Age: The risk increases with age.
- Gender: OA is more common in women.
- Joint injuries: Previous injuries can contribute.
- Obesity: Excess weight can strain joints, especially in the knees.
-
Treatment:
- Medications: Pain relievers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and sometimes corticosteroids.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve joint function and strengthen supporting muscles.
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight management, joint protection techniques, and assistive devices.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be considered.
-
-
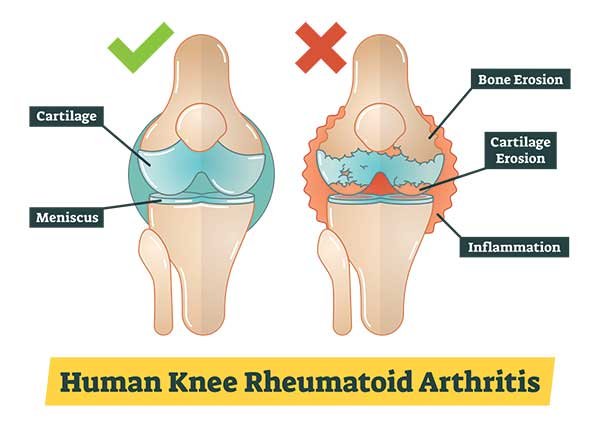
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
-
Causes: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium (the lining of the membranes that surround the joints).
-
Risk Factors:
- Genetics: Family history of RA may increase the risk.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop RA.
- Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor.
-
Treatment:
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): These drugs slow down the progression of RA by suppressing the immune system.
- Biologics: These are a type of DMARD that targets specific pathways in the immune system.
- NSAIDs and Corticosteroids: To manage symptoms like pain and inflammation.
- Physical and Occupational Therapy: To maintain joint function.
-
What's Your Reaction?