Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Diabetes management involves maintaining blood sugar levels within a target range. This typically includes a combination of lifestyle changes, medication (such as insulin or oral medications), and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. Proper nutrition, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight are essential components of diabetes management.
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood.
This occurs when the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or doesn't effectively use the insulin it does produce.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels and allows cells to use glucose for energy.
There are several types of diabetes, but the two most common are:
-
Type 1 Diabetes: This is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to survive. . It is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can develop at any age.
-
Type 2 Diabetes: This form of diabetes is more common and typically develops in adulthood, although it is increasingly being diagnosed in children and adult due to rising rates of obesity. In type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, and the pancreas may not produce enough insulin to compensate for this resistance. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and genetics can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Common symptoms of diabetes include_
Increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow wound healing.
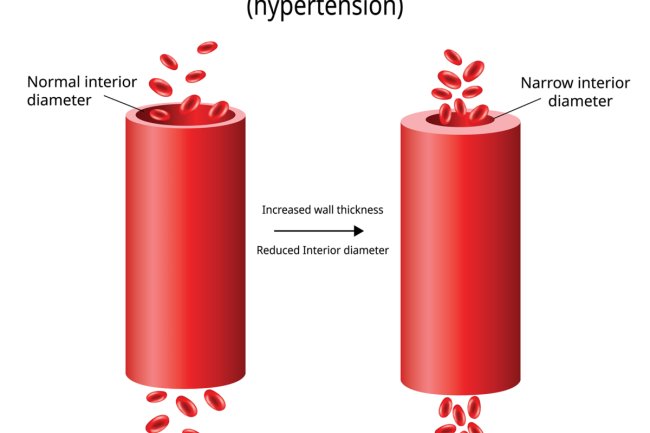
Long-term uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and more.
Diabetes management involves_ maintaining blood sugar levels within a target range.
This typically includes a combination of lifestyle changes, medication (such as insulin or oral medications), and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels.
Proper nutrition, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight are essential components of diabetes management.
What's Your Reaction?